 Max Barroso, PT, DPT, SCS, OSC
Max Barroso, PT, DPT, SCS, OSC Dr. Max Barroso is a licensed physical therapist with a clinical specialty in sports and orthopedics. He treats athletes across the lifespan, with current practice emphasis on college-aged and adult athletes. He is a mentor and clinical instructor for Doctor of Physical Therapy students in Los Angeles, CA, where he practices and resides.
This free guide can help you avoid injury and speed up recovery. Included are general sports injury prevention tips, a look at specific injuries’ causes and treatments, suggestions for low-impact training and more. Read on to enjoy gain with less pain.
Here we look at five ways to reduce the risk of athletic injuries in general. Later on we present prevention tips for ten specific sports injuries.
The most common cause of chronic sports injuries is the failure to warm up. Without warming up, muscles and connective tissues aren’t as flexible as they need to be. Athletic activity then stretches the body before it’s ready, causing muscle rips and other damage.
Your risk of chronic sports injuries can decrease if you lightly work your relevant muscles before adding extra demand. Stretch your body and then spend at least five to ten minutes easing into each activity session.
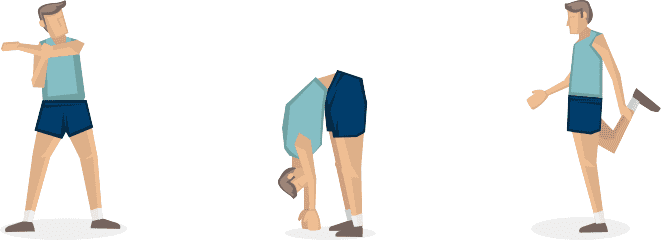
Quick examples of warm-ups: A runner can begin with a focus on leg stretches, then start strolling and gradually pick up speed. A rower can stretch the whole body and then perform partial rows before completing full rowing cycles.
Warming up is essential to sports injury prevention. Additionally the following five behaviors help athletes minimize and prevent damage to their bodies.
Many sports injuries can be healed with simple at-home care, but sometimes it’s important to call a pro as soon as possible. Here we look at when to call a doctor and how to treat common sports injuries at home.
Some sports injuries require immediate professional care. Here are some reasons to call a doctor right away if:
Also contact a doctor if an older sports injury starts to swell or ache again.
The RICE strategy -- Rest, Ice, Compression, Elevation -- is often recommended to reduce swelling, relieve pain and expedite healing. RICE treatment may be most effective when it begins right after injury and continues for at least 48 hours. Here are the steps:
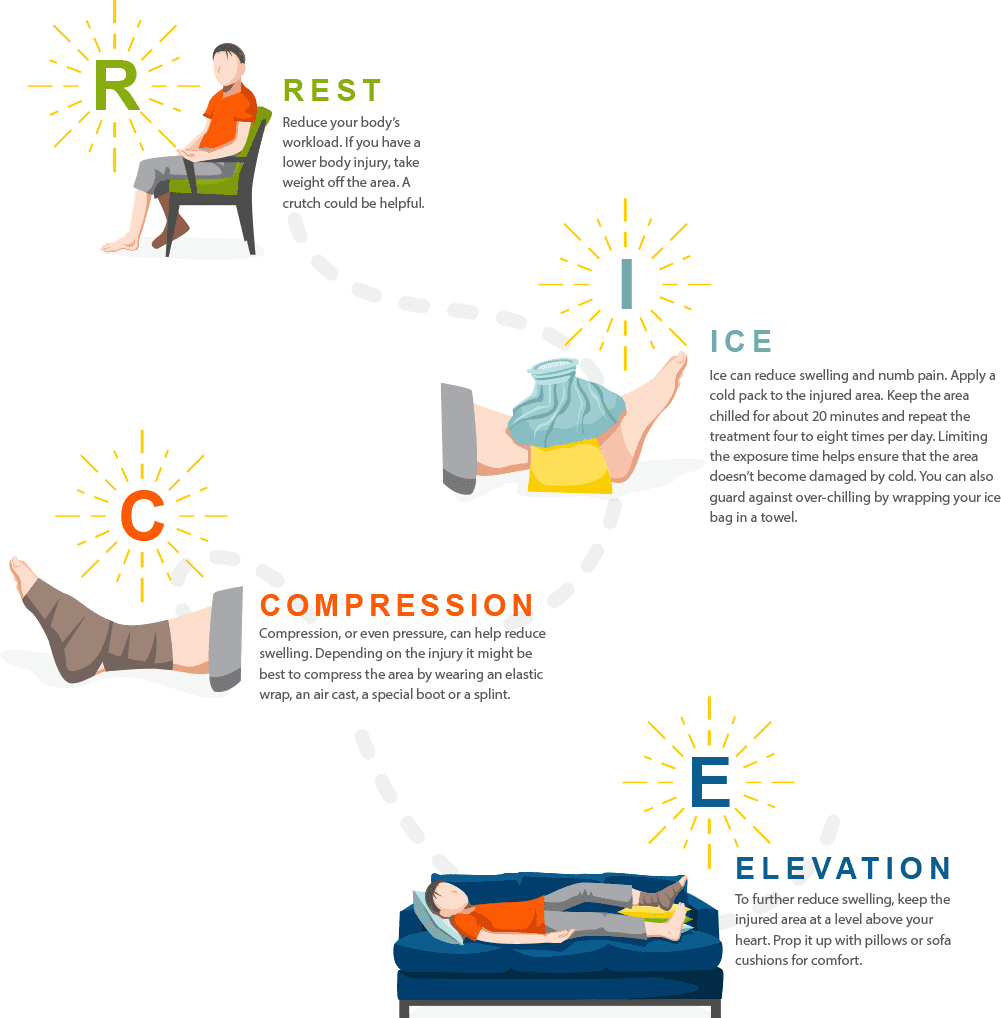
Additionally you might want to take a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug such as ibuprofen or aspirin to reduce swelling and pain. Acetaminophen may also relieve pain but is not effective against swelling.
Don't play through pain! If you play when injured, you will cause more harm.
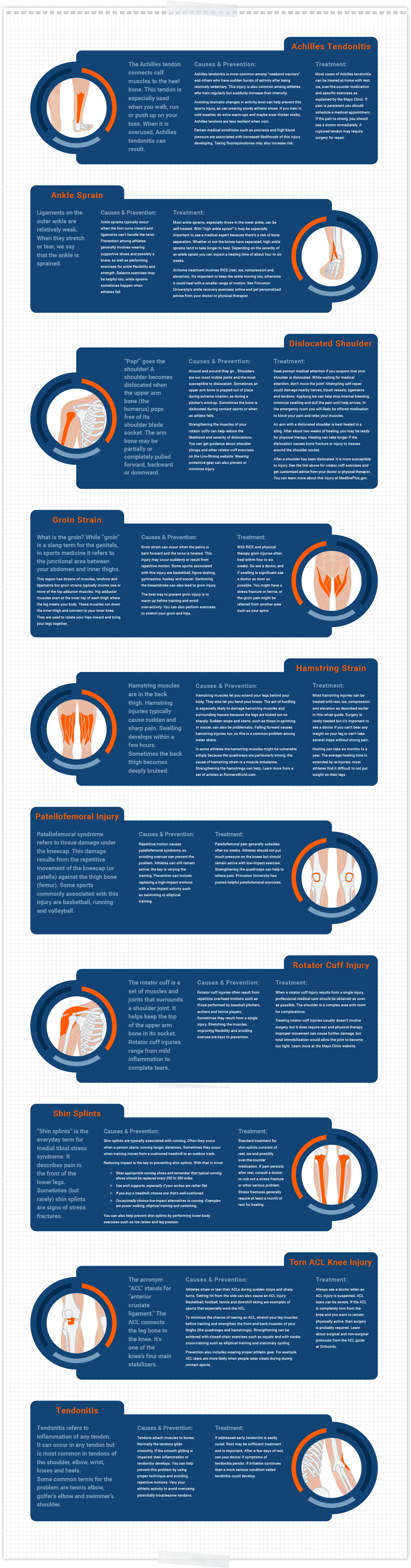
Learn from other athletes’ mistakes and successes. Here are specific sports injuries, how to avoid them and how they’re commonly treated.
A key to sports injury prevention is avoiding overuse of specific muscles and connective tissues. To minimize injury risk, consider substituting your regular sports training with one of the activities below. Each activity provides cardio or endurance training but is “low-impact” or gentle on your frame. The first three activities are resistance strength trainers as well.
The following activities help athletes train for strength and endurance. These cross-training activities are either no-impact or low-impact; their moves don’t jar the body. These activities are lower-risk alternatives to high-impact sports such as basketball, gymnastics and running.
Cycling is a low-impact alternative to running, jumping and contact sports. Of the three types of exercise bikes, recumbent bikes are the gentlest to knees. These bikes let you lean back to pedal and thereby relieve pressure from the spine, hips, knees and ankles. Other options are traditional upright exercise bikes and high-intensity indoor cycle trainers.
The strengthening of shins is a special benefit of cycling for runners prone to shin splints. Typical indoor bikes offer about 20 resistance settings to support different workout objectives.
Elliptical training lets athletes take walking or running strides without strain. With each step the trainee’s body maintains contact with the machine, making cardio exercise low-impact or zero-impact. Benefits include cardiovascular endurance, total-body muscle toning, flexibility improvement and more.
It’s important to use correct form when elliptical training, so be sure to choose a machine with an appropriate stride length. Also have a friend or coach check your gait.
Athletes are sometimes surprised to discover how effectively walking can support their performance goals. This is especially true with incline training, which can be done with steep outdoor paths and with incline treadmills. As mentioned in the elliptical training section above, an incline can seriously boost a workout! Consider the following:
With or without an incline, walking also helps people maintain flexibility. It’s an integral part of many sports rehab plans.
The following activities are low-impact or zero-impact examples of aerobic training. They are useful in both sports injury prevention and sports rehab.
Cross-country ski machines are designed to work all major muscle groups, support endurance training and burn hundreds of calories per hour. Ski machines are also gentle on joints and connective tissues.
A ski machine can be an ideal fit for the athlete concerned about straining the lower body. However, because ski machines involve full extension of the limbs they can be problematic for those with shoulder pain or neck pain.
Pool running or deep water running is a zero-impact activity. It’s accomplished with a flotation device in the deeper end of a pool. With your legs suspended from the pool floor, you can make the motions of running for cardio training without the usual harsh impact on joints. Aim for high speed, such as 180 strides/minute, and be sure to use an upright posture as you would on the road.
While it’s usually reserved for sports rehab, this activity is also an option for everyday low-risk training. After a week or two of pool running, outdoor running times are generally improved.
Swimming is a top alternative to high-impact sports such as running and basketball. It tones all major muscle groups, yet as a non-weight bearing exercise it’s easy on joints and connective tissues.
While swimming is very low impact, certain strokes may be lower-risk than others. People with knee pain should avoid spending much time on the breaststroke. Those with shoulder pain should choose something other than the front crawl or backstroke.
In addition to avoiding overuse of the body, athletes can guard against injury with mobility and stability training. This final section of our sports injury guide has links to tutorials that improve mobility (range of motion) and stability (balance).
Stretches are sometimes called mobility or flexibility exercises. No equipment is required, but stretching can be enhanced with resistance bands and foam rollers. Here are helpful guides to stretching different parts of the body.
Stability exercises help prevent sports injury by minimizing falls. No special equipment is needed but stability balls and medicine balls are useful. See the following websites for stability exercise tips.